IUterusure
DNA Methylation Detection Kit for Endometrial Cancer (cervical exfoliated cell)
- Endometrial cancer is one of the three major malignant tumors of female reproductive system.
- Ranked first among gynecological tumors in developed countries.
- By 2023, there are no guidance-recommended screening methods for endometrial cancer.
0
%
Sensitivity
0
%
Specificity

Current methods have limited sensitivity or are highly invasive
Method | Advantage | Limitation |
|
|
|
ultrasound |
|
|
| Microhistopatholog ical examination |
|
|
Cytologic
| The operation is simple, can effectively reduce endometrial injury, reduce the risk of uterine perforation and uterine infection |
|
| Hysteroscopic localiza- tion biopsy or curettage | Gold standard, high accuracy |
|
Can cervical exfoliated cells detect endometrial cancer?
Endometrial exfoliated cells will accumulate in the uterine cavity, cervical canal and cervix over time. A small amount of endometrial exfoliated cells can be obtained by taking cervical exfoliated cells, and endometrial cancer can be screened through highly sensitive detection methods such as DNA methylation.
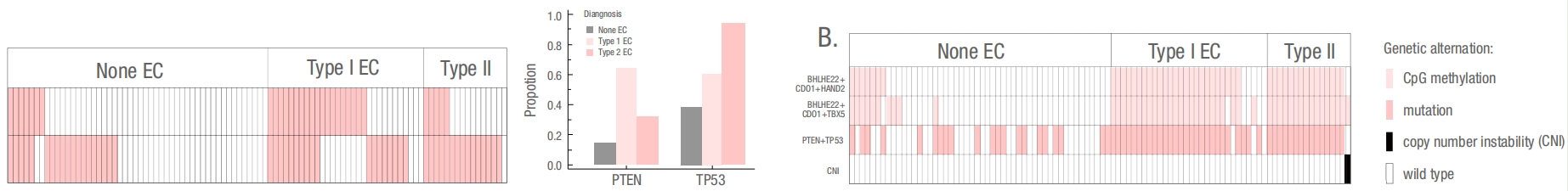
Studies have shown that cervical exfoliated cell gene methylation detection shows good effectiveness in endometrial cancer screening,and in comparison with gene mutations, it is more suitable for endometrial cancer screening.(As shown in the following figure).
Kit Components of IUterusure

Cell-direct Bisulfite Modification Kit

DNA Methylation Detection Kit for Endometrial Cancer
| Brand Name | IUterusure |
| Specimen | cervical exfoliated cell |
| Intended Use | The kit is intended for in vitro qualitative methylation detection of UCECM19 and UCECM22 genes in cervical exfoliated cells of the population at high risk of endometrial cancer. |
Advantage of IUterusure
Simple sampling
IUterusure can be performed on the same sample (self-sample or physician/ gynecologist collected) as the primary screening HPV test.

Small sample volume
Use 100-200ul exfoliated cells as sample type.
High accuracy
The sensitivity for detection of cancer is 98.36%, the specificity is 92.59%.

Easy operation
IUterusure can be performed on the mainstream brand qPCR machine.

Avoid over-treatment
Provide a non-invasive screening method before diagnostic curettage to reduce unnecessary curettage and reduce the potential risk of curettage.

Reduce anxiety
IUterusure provides test negative patients with peace of mind that they have a low short-term risk of Endometrial cancer.
For People
1.High risk group:
Patients with Lynch syndrome, those with third-degree relatives who have Lynch syndrome but have not undergone related genetic testing, and those with a family history of endometrial cancer or colon cancer.
2.People at increased risk:
Lifelong childlessness or primary infertility
Long-term treatment with tamoxifen (especially in patients >50 years old or postmenopausal who are still taking tamoxifen)

Age ≥45 years old, combined with diabetes
Obesity, body fat index (BMI) ≥30 kg/m²

Polycystic ovarian syndrome

History of estrogen use without progesterone antagonism
Late menopause (>55 years old)
3.Other people who are willing to undergo endometrial cancer screening, such as menopausal people.
Testing Procedures
Sample collection
Pretreatment and extraction

Bisulfite conversion and purification

qPCR procedure


Analysis and Report

Sample collection

Pretreatment and extraction


Bisulfite conversion and purification


qPCR procedure


